The response to an injury is inflammation.
This is normal and that is important to note because sometimes inflammation can be misrepresented as being completely bad and pathological.
That is not always the case which is what we will outline below.
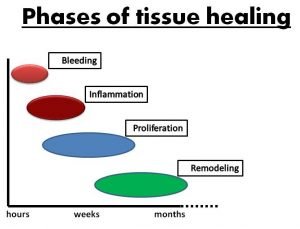
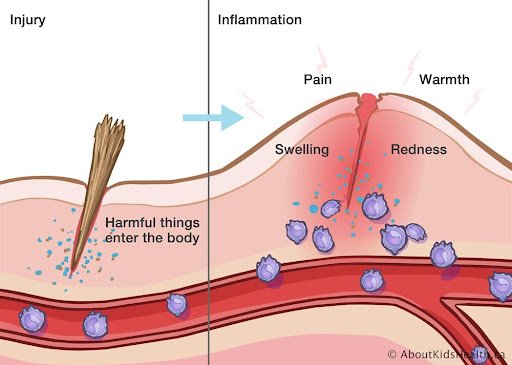
The immediate response to damaged tissue is usually bleeding and swelling. At the cellular level damaged tissue dies and releases a chemical called histamine which increases the rate of fluid flooding the area from the surrounding blood vessels.
This causes dilation of blood vessels surrounding the damaged tissue, allowing movement of white blood cells to the injured site, platelets and other blood products to the damaged tissue – which starts the inflammatory process.
This occurs immediately following tissue damage and is managed in minutes to hours after injury.
What Are The 5 Classic Signs Of Inflammation?
- Pain
- Heat
- Redness
- Swelling
- Loss of Function
What Is The Main Cause Of Inflammation In The Body?
The arrival of blood products to the damaged tissue site allows the body to prepare for the healing process.
White blood cells, specifically leukocytes, infiltrate the damaged tissue and consume debris and dead tissue in a process called phagocytosis.
Once the damaged tissue is removed, the remaining tissue is prepared for rebuilding and the damaged cells no longer produce inflammatory chemicals, slowing down the inflammatory process.
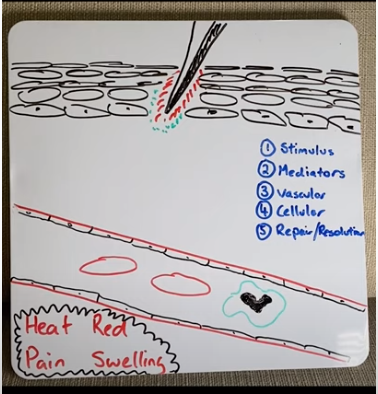
When damaged tissue is unable to be completely cleared or removed from the damage site, inflammation continues to cycle without stopping, this is called chronic inflammation.
The normal process of inflammation spans between minutes following damage and the next 72 hours post injury.
How Do You Get Rid Of Inflammation In Your Body?
In the last stages of inflammation special cells called fibroblasts begin to rapidly multiply in and around the damaged tissue in a process called proliferation.
Fibroblasts reconstruct damaged blood vessels in the area and lay down bundles of collagen to rebuild the damaged tissue at the damage site.
This may include surrounding muscle/connective/epithelial tissues that were also damaged by the abnormal load causing tissue breakdown.
Once the immature tissue is laid down, the wound begins to contract to reduce the size of the damaged site.
This begins on the first day of injury and extends up to a month post injury.

What Is The Strongest Anti-Inflammatory?
This is a big question because there are many ways to answer this question.
From a conservative perspective the best and long lasting measure for reducing inflammation is allowing the natural process to come to a natural end. Conservative healing time frames.
So this comes down to the specific tissue wound healing. Muscles, ligaments, tendons, nerves, discs and all human tissue have a specific healing time frame. Some may take seconds and minutes, others hours and days but most are weeks and months.
My best recommendation for anti-inflammatory effects – check out our PEACE LOVE blog post. It houses all you need to know!
This basic overview explains why inflammation is a normal process and why tissue cannot simply heal overnight but can take weeks to months to fully restore.
As Physiotherapists our job is to manage your expectations regarding normal recovery time frames from injuries and how to best manage your specific condition.
Sometimes despite your best effort medical and surgical assistance may be required for the best possible outcome or safest approach to rehabilitation.
Your Physiotherapist can perform manual therapy to assist with the condition of damaged tissue and instruct on appropriate activity and exercise to facilitate tissue healing.
Make an appointment to see one of our Physiotherapists to help you today!
#MakingHealthySimple
Leki Sisifa

